In mid-2025, Counter Threat Unit™ (CTU) researchers observed a sophisticated BRONZE BUTLER campaign that exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Motex LANSCOPE Endpoint Manager to steal confidential information. The Chinese state-sponsored BRONZE BUTLER threat group (also known as Tick) has been active since 2010 and previously exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Japanese asset management product SKYSEA Client View in 2016. JPCERT/CC published a notice about the LANSCOPE issue on October 22, 2025.
Exploitation of CVE-2025-61932
In the 2025 campaign, CTU™ researchers confirmed that the threat actors gained initial access by exploiting CVE-2025-61932. This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands with SYSTEM privileges. CTU analysis indicates that the number of vulnerable internet-facing devices is low. However, attackers could exploit vulnerable devices within compromised networks to conduct privilege escalation and lateral movement. The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added CVE-2025-61932 to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog on October 22.
Command and control
CTU researchers confirmed that the threat actors used the Gokcpdoor malware in this campaign. As reported by a third party in 2023, Gokcpdoor can establish a proxy connection with a command and control (C2) server as a backdoor. The 2025 variant discontinued support for the KCP protocol and added multiplexing communication using a third-party library for its C2 communication (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Comparison of internal function names in the 2023 (left) and 2025 (right) Gokcpdoor samples
Furthermore, CTU researchers identified two different types of Gokcpdoor with distinct purposes:
- The server type listens for incoming client connections, opening the port specified in its configuration. Some of the analyzed samples used 38000 while others used 38002. The C2 functionality enabled remote access.
- The client type initiates connections to hard-coded C2 servers, establishing a communication tunnel to function as a backdoor.
On some compromised hosts, BRONZE BUTLER implemented the Havoc C2 framework instead of Gokcpdoor. Some Gokcpdoor and Havoc samples used the OAED Loader malware, which was also linked to BRONZE BUTLER in the 2023 report, to complicate the execution flow. This malware injects a payload into a legitimate executable according to its embedded configuration (see Figure 2).
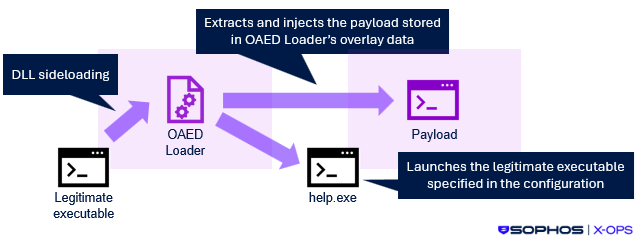
Figure 2: Execution flow utilizing OAED Loader
Abuse of legitimate tools and services
CTU researchers also confirmed that the following tools were used for lateral movement and data exfiltration:
- goddi (Go dump domain info) – An open-source Active Directory information dumping tool
- Remote desktop – A legitimate remote desktop application used through a backdoor tunnel
- 7-Zip – An open-source file archiver used for data exfiltration
BRONZE BUTLER also accessed the following cloud storage services via the web browser during remote desktop sessions, potentially attempting to exfiltrate the victim’s confidential information:
- file.io
- LimeWire
- Piping Server
Recommendations
CTU researchers recommend that organizations upgrade vulnerable LANSCOPE servers as appropriate in their environments. Organizations should also review internet-facing LANSCOPE servers that have the LANSCOPE client program (MR) or detection agent (DA) installed to determine if there is a business need for them to be publicly exposed.
Detections and indicators
The following Sophos protections detect activity related to this threat:
- Torj/BckDr-SBL
- Mal/Generic-S
The threat indicators in Table 1 can be used to detect activity related to this threat. Note that IP addresses can be reallocated. The IP addresses may contain malicious content, so consider the risks before opening them in a browser.
| Indicator | Type | Context |
| 932c91020b74aaa7ffc687e21da0119c | MD5 hash | Gokcpdoor variant used by BRONZE BUTLER (oci.dll) |
| be75458b489468e0acdea6ebbb424bc898b3db29 | SHA1 hash | Gokcpdoor variant used by BRONZE BUTLER (oci.dll) |
| 3c96c1a9b3751339390be9d7a5c3694df46212fb97ebddc074547c2338a4c7ba | SHA256 hash | Gokcpdoor variant used by BRONZE BUTLER (oci.dll) |
| 4946b0de3b705878c514e2eead096e1e | MD5 hash | Havoc sample used by BRONZE BUTLER (MaxxAudioMeters64LOC.dll) |
| 1406b4e905c65ba1599eb9c619c196fa5e1c3bf7 | SHA1 hash | Havoc sample used by BRONZE BUTLER (MaxxAudioMeters64LOC.dll) |
| 9e581d0506d2f6ec39226f052a58bc5a020ebc81ae539fa3a6b7fc0db1b94946 | SHA256 hash | Havoc sample used by BRONZE BUTLER (MaxxAudioMeters64LOC.dll) |
| 8124940a41d4b7608eada0d2b546b73c010e30b1 | SHA1 hash | goddi tool used by BRONZE BUTLER (winupdate.exe) |
| 704e697441c0af67423458a99f30318c57f1a81c4146beb4dd1a88a88a8c97c3 | SHA256 hash | goddi tool used by BRONZE BUTLER (winupdate.exe) |
| 38[.]54[.]56[.]57 | IP address | Gokcpdoor C2 server used by BRONZE BUTLER; uses TCP port 443 |
| 38[.]54[.]88[.]172 | IP address | Havoc C2 server used by BRONZE BUTLER; uses TCP port 443 |
| 38[.]54[.]56[.]10 | IP address | Connected to ports opened by Gokcpdoor variant used by BRONZE BUTLER |
| 38[.]60[.]212[.]85 | IP address | Connected to ports opened by Gokcpdoor variant used by BRONZE BUTLER |
| 108[.]61[.]161[.]118 | IP address | Connected to ports opened by Gokcpdoor variant used by BRONZE BUTLER |
Table 1: Indicators for this threat
